 McAfee antivirus software may need to be removed for various reasons. Not the least of which it causes dysfunction in your software environment, acts like a virus itself and slows your computer down to a crawl.
McAfee antivirus software may need to be removed for various reasons. Not the least of which it causes dysfunction in your software environment, acts like a virus itself and slows your computer down to a crawl.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to uninstall McAfee from your Windows 11 system:
Step 1: Access Settings
Click on the Start Menu located at the bottom left corner of your screen.
Select the gear-shaped Settings icon to open the Settings menu.
Step 2: Open Apps
In the Settings menu, select Apps from the list on the left-hand side.
Step 3: Locate McAfee Software
Scroll down the list under “Apps & features” to find the McAfee antivirus software.
Click on the McAfee application to reveal the options.
Step 4: Uninstall McAfee
After selecting McAfee, a submenu will appear. Click on the Uninstall button.
Step 5: Confirmation Prompt
A confirmation prompt will appear asking if you want to allow this app to make changes to your device. Click Yes to proceed with the uninstallation.
Step 6: McAfee Uninstallation Process
The McAfee uninstaller will open. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation process. This may involve confirming your choice and waiting for the software to be removed from your system.
Step 7: Reboot Your System (if prompted)
After the uninstallation is complete, you may be prompted to restart your computer. If so, click on the Restart Now button to reboot your system.
Step 8: Verify McAfee is Uninstalled
Once your system restarts, check the Apps list in Settings again to ensure McAfee is no longer listed among your installed applications.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully uninstalled this garbage from your Windows 11 computer.
Does the Dell XPS 8940 Support Gen 5 M.2 Drives?
Recently, I got this question from a client. No, the Dell XPS 8950 desktop computer does not support Gen 5 M.2 PCIe SSDs. The motherboard in the XPS 8950 is the Dell Z960, which only supports up to Gen 4 PCIe. This means that while you can use a Gen 4 M.2 PCIe SSD in your XPS 8950, you will not be able to take advantage of the faster speeds that Gen 5 SSDs offer.Here are some resources that confirm this:
Dell XPS 8950 Manual: The manual for the XPS 8950 states that the M.2 slots support PCIe Gen 3 x4 and PCIe Gen 4 x4 SSDs, but makes no mention of Gen 5 support.
Dell XPS 8950 Specifications: The specifications page for the XPS 8950 on the Dell website also lists the M.2 slots as supporting PCIe Gen 3 x4 and PCIe Gen 4 x4 SSDs.
Dell Community Forum: There is a thread on the Dell Community Forum where users have discussed the fact that the XPS 8950 does not support Gen 5 M.2 PCIe SSDs.
If you are looking for a desktop computer that supports Gen 5 M.2 PCIe SSDs, you will need to choose a different model. Some newer Dell XPS models, such as the XPS 8960, do support Gen 5 M.2 PCIe SSDs.
What is Bitlocker and How to Turn It Off?
 BitLocker is a security feature in Windows that allows you to encrypt your hard drive to protect your data from unauthorized access. When you enable BitLocker, you are required to generate a recovery key to unlock your encrypted drive in case you forget the password or encounter a system failure. The problem is you usually only encrypt the data against yourself. TURN IT OFF. Unless you’re in the FBI or a top secret industry and usually even then it’s only going to cause you a problem later on.
BitLocker is a security feature in Windows that allows you to encrypt your hard drive to protect your data from unauthorized access. When you enable BitLocker, you are required to generate a recovery key to unlock your encrypted drive in case you forget the password or encounter a system failure. The problem is you usually only encrypt the data against yourself. TURN IT OFF. Unless you’re in the FBI or a top secret industry and usually even then it’s only going to cause you a problem later on.
Here’s a guide on how to turn off BitLocker encryption:
1. Open the Control Panel: Click on the Start button and select Control Panel from the menu. Alternatively, you can search for Control Panel in the Windows search bar.
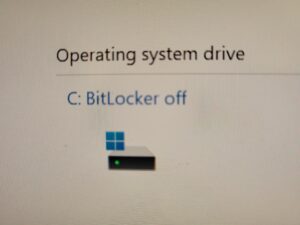
2. Click on “System and Security”: In the Control Panel, click on “System and Security” to access the BitLocker Drive Encryption settings.
3. Turn off BitLocker: Under the BitLocker Drive Encryption section, you’ll see an option to “Turn off BitLocker.” Click on this option to begin the process of turning off the encryption.
4. Enter the recovery key: If prompted, you will need to enter the recovery key that you created when you initially set up BitLocker. This key is crucial for unlocking the encrypted drive when BitLocker is turned off.
5. Turn off BitLocker for the drive: After providing the recovery key, you will be given the option to turn off BitLocker for the selected drive. Select the drive that you want to disable BitLocker for and click “Turn off BitLocker.”
6. Confirm turning off BitLocker: You will then be prompted to confirm the action of turning off BitLocker encryption. Click “Decrypt the drive” to confirm and initiate the process of decrypting the drive.
7. Wait for decryption: Depending on the size and speed of your drive, the decryption process may take some time. It’s important not to interrupt this process, as doing so could result in data loss or corruption.
Once the decryption process is complete, your drive will no longer be encrypted with BitLocker. You will no longer need to enter your recovery key to access your files, and the encryption key will be turned off.
A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the History and Purpose of Web Browsers
 In today’s digital age, web browsers have become an essential tool through which we access information, communicate with others, and navigate the vast landscape of the internet. While influential browsers such as Edge, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Safari, and Firefox dominate the market, the historical evolution and underlying purposes of these browsers have significantly shaped our online experiences. This article aims to take you on a captivating journey through time, exploring the origins, milestones, and distinct features of these popular web browsers.
In today’s digital age, web browsers have become an essential tool through which we access information, communicate with others, and navigate the vast landscape of the internet. While influential browsers such as Edge, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Safari, and Firefox dominate the market, the historical evolution and underlying purposes of these browsers have significantly shaped our online experiences. This article aims to take you on a captivating journey through time, exploring the origins, milestones, and distinct features of these popular web browsers.
I. The Early Days: From Mosaic to Internet Explorer
The web browsing journey began with Mosaic, a pioneering browser developed in the early 1990s by the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA). However, it was Internet Explorer (IE), released in 1995 by Microsoft, that played a pivotal role in familiarizing the masses with web surfing. As the default browser on Windows, IE quickly achieved widespread adoption while embodying the basic web browsing principles of that era.
II. The Rise of Firefox and Safari
In 2004, Mozilla Firefox emerged as a strong contender in the browser market, offering enhanced security, privacy, and customization options. Built upon open-source principles, Firefox challenged the dominance of IE and introduced a more user-centric experience. Around the same time, Apple introduced Safari, exclusively for Mac systems. Safari swiftly gained popularity due to its efficient performance, sleek design, and seamless synchronization with other Apple devices.
III. Chrome’s Revolution: Speed, Simplicity, and Stability
In 2008, Google Chrome entered the arena, revolutionizing web browsing with its minimalist design, speed, and stability. By introducing a multiprocess architecture, Chrome improved performance and security, allowing users to enjoy a seamless browsing experience. Chrome quickly became the browser of choice for many, dominating the market with its continuous updates and offering extensive customization through a range of extensions.
IV. Edge: Microsoft’s Modern Reinvention
As the successor to Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge made its debut in 2015, aiming to bring a fresh and modern browsing experience to Windows users. Determined to provide speed, security, and compatibility, Edge was designed to be a lightweight, user-friendly browser. Embracing the Chromium open-source project in 2018 brought significant improvements, enabling Edge to compete with other popular browsers, offering a customizable interface and an extensive library of extensions.
V. The Broader Impact: Advancing Web Standards and User Experience
While each browser has its unique features and design, collectively, these web browsers have worked towards advancing web standards, improved security, and a seamless user experience. Through various iterations, they have pushed the boundaries of web browsing, enabling compatibility with emerging technologies, such as HTML5, CSS, JavaScript, and more.
Conclusion:
Web browsers have come a long way since their inception, continually adapting to meet the evolving needs of users and the challenges posed by an ever-changing internet landscape. From Internet Explorer’s pioneering dominance to the sophistication of Edge, Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, each browser has played a crucial role in making the web accessible to billions of people worldwide. As technology and user requirements continue to evolve, the future of web browsing promises further innovation and optimization, ensuring an even richer online experience for all.
Cracking the Code: Unraveling 10 Uncommon Factors Affecting Your Home Network
 Introduction: In the era of advanced technology and increasing reliance on home networks for various tasks, encountering network issues can be frustrating. While most common network problems can be easily resolved, there are a few lesser-known culprits that may be affecting your home network performance. Take a deep dive with us as we explore ten unique factors that might be playing a role in your network troubles.
Introduction: In the era of advanced technology and increasing reliance on home networks for various tasks, encountering network issues can be frustrating. While most common network problems can be easily resolved, there are a few lesser-known culprits that may be affecting your home network performance. Take a deep dive with us as we explore ten unique factors that might be playing a role in your network troubles.
1. Aged Firmware: Outdated firmware in your router can cause compatibility issues and hinder network performance. Ensure you regularly update your router’s firmware to stay ahead of potential problems.
2. DNS Hiccups: Domain Name Server (DNS) servers play a vital role in translating websites’ domain names to IP addresses. Opting for unreliable or overloaded DNS servers might result in sluggish network speeds. Switching to reliable and fast DNS servers like Google DNS or Cloudflare DNS can help mitigate this issue.
3. Overburdened Network: An overcrowded network can impede your home network’s performance. Multiple devices simultaneously accessing the network can lead to congestion, slower speeds, and intermittent connectivity. Consider implementing Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize critical devices or upgrade your internet package.
4. Sneaky Signal Interference: Unbeknownst to many, various household objects can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Mirrors, metal objects, thick walls, and even larger appliances can disrupt signal strength. Assess your network placement and consider relocating your router to minimize interference.
5. Struggling Network Adapter: Outdated or malfunctioning network adapters can lead to poor network connectivity and speed. Ensure your devices are equipped with up-to-date and compatible network adapters to prevent this bottleneck.
6. Invasive Malware: Malware isn’t limited to affecting computers; it can also target routers. Malicious code injected into routers can compromise network security, degrade performance, and even redirect your internet traffic. Regularly update your router’s firmware, change default login credentials, and install reputable security software to ward off potential malware threats.
7. Unoptimized Wi-Fi Channels: Interference from neighboring wireless networks can slow down your Wi-Fi speeds. Using tools like Wi-Fi analyzers, identify the least congested channels and switch your Wi-Fi router to an optimized channel for improved performance.
8. Weather Woes: Extreme weather conditions such as heavy rain, intense lightning storms, or severe winds can physically damage or disrupt network equipment, leading to intermittent or complete network outages. Safeguard your networking equipment by ensuring proper insulation and protection from the elements.
9. Cryptic Cable Faults: Damaged or frayed network cables can cause connectivity issues. Ensure all cables are securely connected, properly insulated, and free from physical damage to maintain a reliable network connection.
10. Resource-Hungry Background Apps: Often overlooked, resource-intensive background applications on your devices can consume a significant portion of your network’s bandwidth, leading to slower internet speeds for other devices. Monitor and manage these apps, limiting their impact on your network performance.
Conclusion: Network issues can stem from various unexpected factors. By understanding the less common culprits affecting your home network, you can troubleshoot more effectively and address these issues proactively. Remain vigilant, keep your devices updated, and make informed decisions to ensure a stable and optimized home network experience.


