
As technology continues to advance at an exponential rate, the demand for individuals with strong computer and IT skills also rises. One way to establish credibility in this fast-paced industry is to obtain relevant certifications. For young people who are just beginning their journey in this field, there are several certifications that they can consider getting as a prerequisite education. Here are some of the certifications worth considering:
1. CompTIA A+
CompTIA A+ is a foundational certification that covers essential computer hardware and software technologies. It is ideal for young people who are beginning their careers in the computer service and repair industry. Through this certification, candidates will learn about installing, configuring, troubleshooting, and repairing PCs, mobile devices, and various other hardware and software components.
2. CompTIA Network+
CompTIA Network+ is an entry-level certification that focuses on networking technologies and concepts. It covers topics such as network design, network protocols, network security, and various other networking-related topics. This certification is ideal for young people who want to pursue a career in the IT field.
3. Microsoft Certified Solutions Associate (MCSA)
MCSA is a Microsoft certification that covers various aspects of Microsoft technologies, including Windows, server administration, and database technologies. This certification is ideal for young people who want to specialize in Microsoft technologies.
4. Amazon Web Services (AWS) Certified Solutions Architect
AWS Certified Solutions Architect is a certification that’s designed to validate the skills and knowledge needed to design and deploy scalable, highly available, and fault-tolerant systems on the AWS platform. This certification is ideal for young people who want to specialize in cloud computing.
5. Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
CCNA is a certification that covers networking concepts and technologies, including routing, switching, security, and troubleshooting. This certification is ideal for young people who want to specialize in networking and network administration.
6. Best Buy Hardware Center Worker
I always tell people that if they are interested in hardware they should check with Best Buy about working at a hardware center. Unlike the Geek Squad which works in store and does software repairs and hardware sales the Hardware Center Workers focus on motherboard repairs, DJ jack repairs, laptop screen replacement’s, ram upgrades, and other things “hardware.”
In conclusion, obtaining relevant certifications can help young people establish credibility in the computer service and repair industry and the IT industry. By earning these certifications, young minds can gain valuable experience and knowledge that is beneficial for their future careers. So, if you’re a young person interested in pursuing a career in the computer and IT industry, consider obtaining the certifications mentioned above. These certifications will not only enhance your resume but will also help you develop the necessary skills to excel in this field.
The Mysterious Malfunction: 7 Reasons Why Motherboards Fail

Motherboards, the core component of a computer system that connects and controls all the other hardware and software, can fail for various reasons, from simple wear and tear to sudden and catastrophic events. Understanding the causes of motherboard failure can help you prevent or troubleshoot common issues and make informed decisions about repair or replacement. Here are seven factors that can contribute to motherboard malfunctions:
1. Power surges and outages.
One of the most common and damaging factors that can affect a motherboard is a power surge or outage. A power surge happens when the voltage of the electrical supply spikes above the normal level, often due to lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations. A power outage occurs when the supply of electricity is suddenly interrupted, either by a blackout, a brownout, or a circuit breaker trip. Both situations can cause the delicate circuits and capacitors on the motherboard to overload or short, leading to permanent damage or data loss.
2. Overheating and cooling.
Another major factor that can impact the health of a motherboard is the temperature. Modern computer systems generate a lot of heat, especially when running resource-intensive applications or games, and require effective cooling systems to dissipate the heat. If the cooling system, such as the fan or the heatsink, fails or gets clogged with dust and dirt, the motherboard can overheat and produce errors or shutdowns. Conversely, if the motherboard is exposed to extremely cold or humid environments, it can suffer from condensation or frost, which can also cause corrosion or short circuits in the components.
3. Static electricity.
Static electricity, the buildup and discharge of electric charges that can occur when objects rub against each other, can also harm motherboards. When you touch a motherboard or any other electronic device, you can transfer static charges that exceed the safe levels and damage the sensitive components. To prevent this, you should always ground yourself, remove any synthetic fabrics or materials, and use an anti-static wrist strap or mat. Even small static shocks can have cumulative effects on the motherboard over time.
4. Age and usage.
Like any other mechanical or electronic device, motherboards have a limited lifespan and can wear out over time with regular usage. The precise duration and quality of a motherboard depend on many factors, such as the brand, model, materials, manufacturing process, and environmental conditions. However, a motherboard that has been used for several years or has undergone many upgrades or repairs is more likely to show signs of degradation, such as slower performance, intermittent crashes, or hardware conflicts.
5. Environmental factors.
Other environmental factors can also affect the stability and safety of a motherboard. For example, exposure to moisture, dust, smoke, and chemicals can damage the circuits and connectors, as well as attract pests or rodents that can chew on the wires or components. Moving a computer system frequently, especially during operation, can also cause mechanical stress or dislodgement of parts. Finally, using incompatible or faulty components, such as RAM, CPU, or power supply, can put additional strain on the motherboard and cause irreparable damage.
6. Malfunctioning peripherals.
Sometimes, a motherboard failure can be caused by a peripheral device, such as a graphics card, sound card, or USB drive. If one of these devices fails or misbehaves, it can send incompatible or excessive signals to the motherboard, disrupting its normal operation or causing it to shut down. To rule out this possibility, you should disconnect or replace any recent peripheral devices and see if the motherboard still exhibits the same symptoms.
7. Manufacturing defects.
Finally, some motherboards can fail due to defects or errors in the manufacturing process. This can happen despite rigorous testing and quality control procedures, and may affect only a small percentage of the products. However, if you suspect that your motherboard has a manufacturing defect, you should contact the manufacturer or the retailer and ask for a warranty replacement or repair.
In conclusion, motherboards can fail for many reasons, some of which are preventable or reversible with proper care and maintenance, while others require professional diagnosis and treatment. By keeping your computer system clean, cool, and grounded, and by using reliable and compatible components, you can help extend the life of your motherboard and avoid costly repairs or replacements.
What is the New Wi-Fi 6 and Do I Need it for My Home Network?

As the world becomes more dependent on digital connectivity, Wi-Fi has become an essential part of our daily lives. With the increasing demand for high-speed, reliable internet, the technology behind Wi-Fi is constantly evolving. This is where Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 come into play.
It’s noteworthy that the Wi-Fi Standards (Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, etc.) are kind of like “generations” and are set by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). This is so we can have uniform standards in the industry which aids in communication, manufacturing, research, implementation, etc. Furthermore, it’s worth mentioning that these are different from (and often confused for) the frequency bands of 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz that your wi-fi router uses. Finally, these standards are not the same thing as your download speeds (measured in MBPS) or signal density (measured as bars that represent a percent of gain or loss of signal).
Wi-Fi 5, also known as 802.11ac, was introduced in 2013 and provided faster speeds, improved performance in crowded areas, and better power efficiency than its predecessor, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n). The maximum theoretical data transfer rate of Wi-Fi 5 is 3.5 Gbps, with support for up to eight spatial streams.
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest standard in wireless networking technology that was introduced in 2019. It is designed to address the increasing demand for faster and more reliable network connections, especially in heavily populated areas. Wi-Fi 6 offers a maximum theoretical data transfer rate of up to 9.6 Gbps and supports up to 12 spatial streams.
One of the most significant differences between Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 is the use of a newer technology known as Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA). OFDMA allows multiple devices to be served simultaneously by splitting channels into smaller subchannels. This means that Wi-Fi 6 networks can efficiently handle many devices at once, reducing network congestion and improving the overall user experience.
Another key difference between the two standards is the improved signal strength and range offered by Wi-Fi 6. With its ability to increase efficiency and reduce interference, Wi-Fi 6 can provide better coverage and range in comparison to Wi-Fi 5. This ensures that users can experience fast and reliable internet connections, even at a distance from the router.
Finally, Wi-Fi 6 also introduces a new feature called Target Wake Time (TWT), which enables devices to conserve battery by scheduling when they wake up and communicate with the network. This reduces power consumption and can lead to longer battery life for connected devices.
In conclusion, Wi-Fi 6 is a newer, faster, and more efficient standard of wireless networking technology. When compared to Wi-Fi 5, it offers higher speeds, better range, improved power efficiency, and the ability to handle more devices at once. As more devices become connected to the internet, these improvements will be increasingly important in ensuring a smooth and reliable user experience for everyone.
Bard vs ChatGPT: What’s the Difference?
Bard is a new AI language model developed by Google researchers. It mainly focuses on generating creative and engaging content, such as poems, stories, and songs, that can mimic human-like writing styles. It is trained on a large-scale corpus of text data and can generate novel text by completing incomplete sentences from given prompts.
On the other hand, Chat GPT is an AI language model from OpenAI that is primarily used for generating text-based conversations. It is designed to replicate human-like chat and conversation styles and is trained on massive datasets to learn subtle nuances in human conversation.
One of the key differences between the two models is their training data. Bard is trained mostly on creative writing, while Chat GPT is trained on a mix of formal and informal text data. This difference in training data reflects in their respective capabilities. Bard can generate engaging creative writing, while Chat GPT excels at generating natural-sounding conversations.
Bard is also unique in that it incorporates a rhyme scheme into its outputs that are rarely produced by Chat GPT, making it more suitable for generating creative content like poems and song lyrics. However, Chat GPT is capable of conversing or answering a wide range of questions in natural vernacular language, while Bard Google wouldn’t be able to do so with as much fluency and accuracy.
Lastly, while both models share a common goal of producing human-like language outputs, their intended use cases are different. Bard is a creative writing tool that can generate catchy and poetic content, while Chat GPT is better suited for generating human-like conversations and providing quick answers to common questions.
In conclusion, while both Bard and Chat GPT are cutting-edge AI language models powered by sophisticated natural language processing technology, their respective differences lie in training data, output capabilities, and intended use cases. Both models provide value in different areas and demonstrate the significant strides made in AI language generation.
Did You Just Get Hacked? No, Probably Not.
As a computer service company owner in Louisville, KY. for the past few years the prevalence of people calling me saying “I’m hacked” has continued to escalate. As technology continues to rapidly advance, cybersecurity threats become more prevalent. However, it is not usually the case that your computer is hacked. Often, people mistakenly blame hacking for a problem that is their own fault.
Here are some examples of such scenarios:
1. Forgotten Passwords: Many times, users lose access to their accounts due to forgetting their password. Instead of seeking assistance from the platform, they tend to believe that a hacker breached their account. Most of them do not realize that they have simply forgotten their password or have forgotten they changed it and blame hackers for a user created problem.
2. Third-Party Programs and Garbage Software: Many users install applications or software from various websites without verifying their authenticity. I routinely find machines with anywhere from one to twenty pieces of garbage software installed. Often the user is playing games when doing this but the software can come from other sources. It can also be bundled with legitimate software, as well. Therefore, it is vital to install applications from trusted sources only or check with a local computer service company about any suspicious software that seems to have “appeared” out of nowhere.
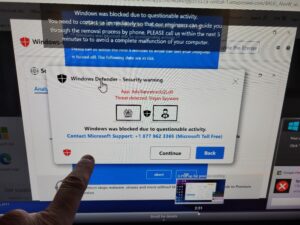
3. People routinely call 1-800 numbers after they have accidently landed on a fake website on the internet or getting a browser infection that won’t let them close their browser.
Often times these sites sound an alarm and tell the user they have done something wrong and need to contact Microsoft, Norton, or other trusted websites via the number on the screen. This is not a hack – it’s a straight-out scam. If you call the number and give remote access to your computer you can be conned out of a payment for bogus services or even your entire bank account.
4. Sometimes I get a call from a customer claiming “My Facebook was hacked.” This is rarely the case. Usually, a third part has right clicked on the photo, set up a new Facebook Page on your behalf, and attempted to add your friends back so they can later attempt to scam your friends out of money. This is not a hack – it’s more a forgery, rather.
In conclusion, users should avoid blaming hackers for every issue that they face regarding their digital devices. Malware, tech support scams, IRS scams, bogus sham and scam phone calls, fake Facebook pages, phishing emails, drive-by browser pseudo-infections, and other scam attempts are just a few of the risks internet users face and mistake for hacking.
It is increasingly essential for computer users to educate themselves of online risks and take necessary cybersecurity measures to protect themselves. Also, you might want to think about getting a local computer repair and service person they trust so they can have a consultant to discuss these matters. But remember – you probably weren’t hacked – you probably just made a bad decision.


